The company J. C. J. Ruiter-Wever was founded in 1944 by Jan Ruiter at the end of World War II. In 1963 the company was continued by his 2 sons who then went apart in 1988. From that moment on, son Jan Ruiter and his wife Carla Wever continued together as J. C. J. Ruiter-Wever in Andijk. The company is currently run by their 2 sons Niels and Stef. Both parents withdrew from the board of management in 2012 in order not to hinder the entrepreneurial drive of their sons. With the 3rd generation at the helm, the company now grows about 90 ha of tulips in France, Noord-Holland and Drenthe. Besides the cultivation they also export tulip bulbs to America, Canada, Poland and Russia. For this purpose, bulbs are also purchased and about 50 to 60 million bulbs are traded annually.In the winter months, the company produces some 13 million tulip flowers from December to May. These are all packaged according to the wishes of the customer and traded off. In total, the company trades approximately 20 million flowers.
J.C.J. Ruiter – Wever

Sustainability
Water
95% of the rainwater from yard and roofs and 100% of the water from processes within the company is collected in a water storage facility under own control. So nothing ends up in the surface water. The collected water is used for various applications within the company, such as casting water for growing the product, flushing sanitary facilities, process water and rinsing bulbs after harvesting. Rainwater is actually used for everything, except for human consumption. For the cultivation in the greenhouse, computer-controlled water is given according to the product’s requirements, in order to use a minimal amount of rainwater and fertilizer. The water and the tank are disinfected with chlorine and hydrogen peroxide as these agents are biodegradable. Climate cells are cooled using the cold from ground water instead of energy, that is often used in conventional cooling.
Thanks to condensing boilers the residual heat from waste gases can be utilized. All tractors in the company are equipped with clean engines with ad-blue technology.
All packaging waste is cleaned and pressed if necessary. The pressed material is offered separately for sustainable recycling.
In order to prevent breeding meadow birds from being disturbed, employees working on the field pay attention to the various “natural movements” of the birds in the field. This way, employees can work around their nests.
When tulips are grown on the field, a crop-free zone of at least 0.5 metres is maintained along water edges in order to prevent plant protection products from entering the surface water.
For bulp production in the fields, only a few crop protection products are used, but during the production from bulb to flower no plant protection product is used at all. Ruiter-Wevers sustainable way of growing is therefore appreciated as particularly good by the accredited organisations issueing certificates.
Energy
The greenhouses are equipped with the most modern climate systems and energy screens. By mixing outside air with air from the greenhouse, a good climate for the tulip bulbs is created in a sustainable way. The fully automated container system on which the tulips are grown ensures optimal greenhouse utilisation and minimal energy requirements per tulip.

People
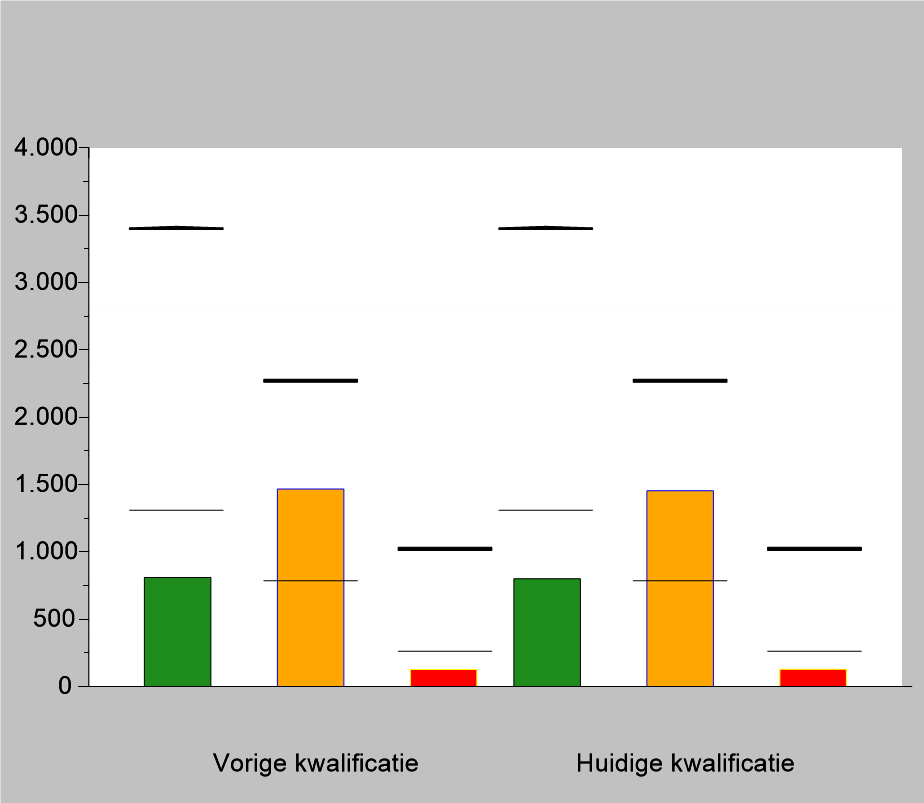
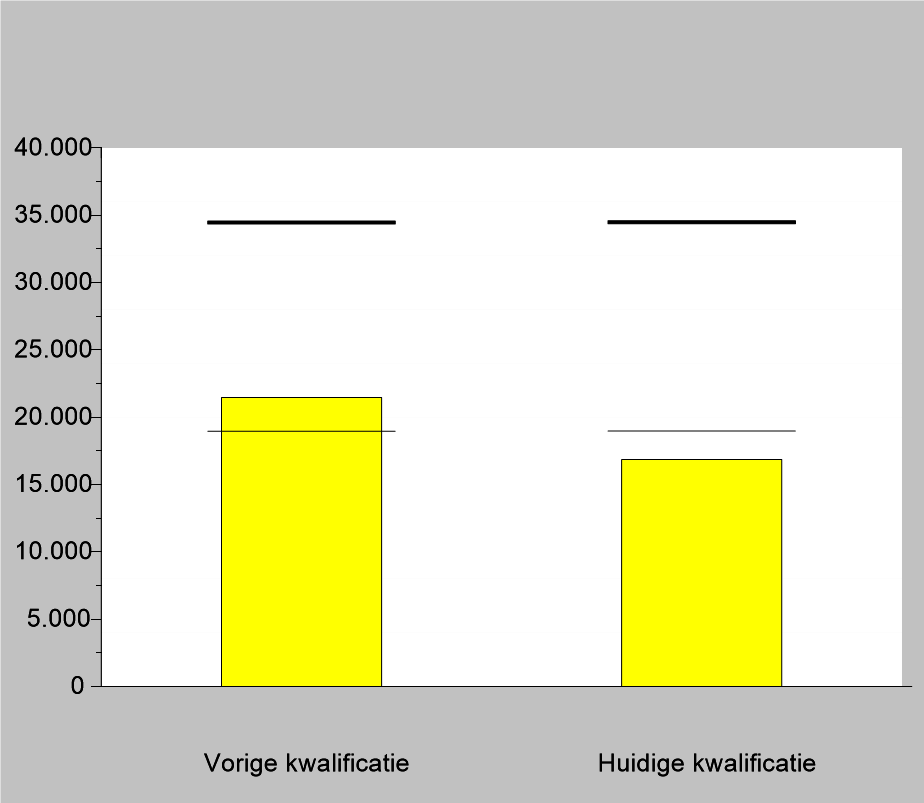
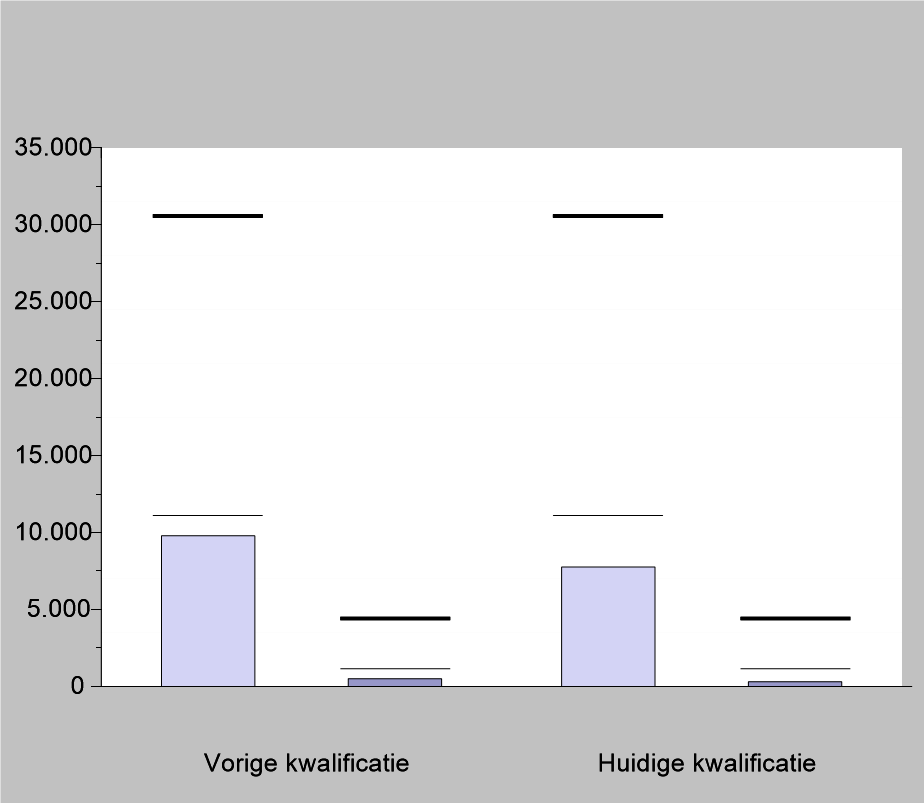
Ruiter-Wever permanently employs 7 people. In peak times at least 30 temporary agency workers will be added. All staff are at least remunerated and paid according to the standards of the Collective Labour Agreement for glasshouse horticulture or for wholesale trade flowers and plants. Within the company, everyone (if deemed eligible) is given the opportunity to grow to a different position.
It is currently being examined whether it is possible to accommodate labour migrants at a suitable location on the company itself. This is to ensure that the staff is housed in proper living conditions without disrupting the housing supply in the area.
Within the company, various attempts are made to involve the employees in the company and in the product. A good social relationship between the employees is highly appreciated.

Health

Care
Tulip: